Tongue tie and lip tie are common conditions that affect infants, but they can also impact older children and adults if not addressed. Both conditions occur when the tissues that connect the tongue or lip to the mouth are too tight, restricting movement. Breathing, speech, and eating issues may result from this. If left untreated, these conditions can have lasting effects on a person’s oral health and development. In addition to discussing the importance of tongue tie removal and other treatment methods, this article will examine the distinctions between lip ties and tongue ties.
What is a Tongue Tie?
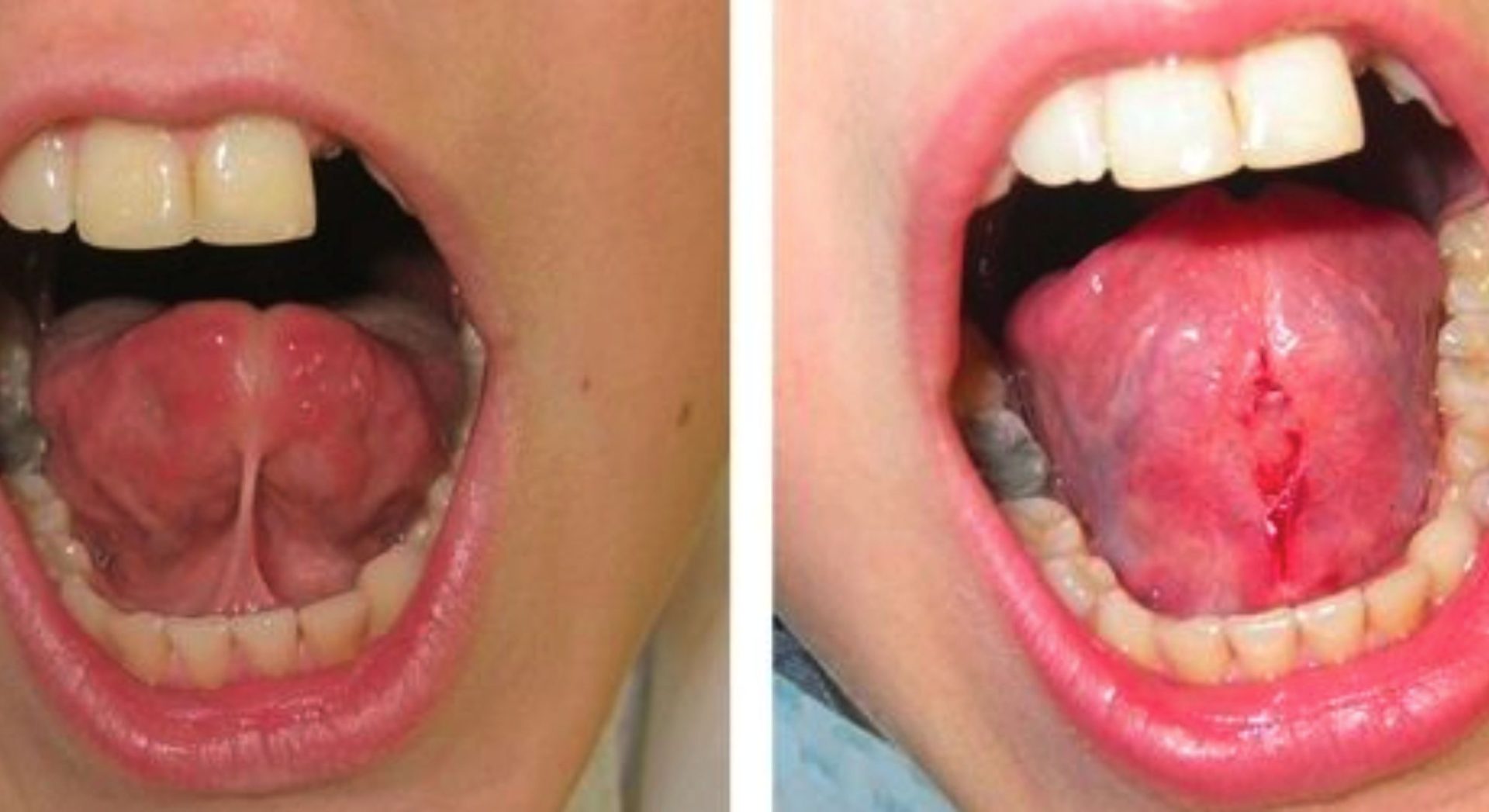
When the frenulum, the band of tissue behind the tongue, is excessively tight or short, it can cause ankyloglossia, often known as a tongue knot. This restricts the tongue’s movement, making it difficult for the tongue to move freely. In infants, this can affect breastfeeding, as the baby may not be able to latch properly, leading to poor feeding, discomfort for the mother, and inadequate milk intake.
In older children or adults, a tongue tie can interfere with speech, causing difficulties with pronouncing certain words or sounds, such as “t,” “d,” “l,” or “r.” It can also impact oral hygiene, as the restricted movement of the tongue may make it harder to clean the teeth effectively.
What is a Lip Tie?
Though it affects the top lip, a lip tie is comparable to a tongue tie. It happens when the frenulum, which connects the gums and top lip, is abnormally thick or taut. In infants, a lip tie can cause issues with breastfeeding, as the baby may struggle to form a proper seal on the breast. This can lead to pain for the mother, along with insufficient milk intake for the baby.
In older children and adults, a lip tie may cause problems with dental health. Gum recession and the exposure of the tooth roots may result from the tight frenulum pulling on the gums. Additionally, a lip tie may contribute to speech issues, although this is less common than with tongue ties.
Symptoms of Tongue Tie and Lip Tie
Both conditions can lead to a variety of symptoms, though they tend to affect different aspects of oral function.
Tongue Tie Symptoms:
- Difficulty breastfeeding, with the infant unable to latch properly or causing pain to the mother.
- Trouble with sucking, swallowing, or swallowing solids.
- Speech difficulties, particularly with certain sounds like “s,” “r,” “t,” and “d.”
- Dental problems, such as cavities, due to difficulty cleaning the teeth.
Lip Tie Symptoms:
- Difficulty breastfeeding, with the baby unable to form a proper latch or causing nipple pain.
- Gaps between the upper teeth, often at the midline.
- Gum recession along the upper gums.
- Speech issues, though this is less common than with tongue tie.
- Oral hygiene difficulties due to restricted lip movement.
How is Tongue Tie Removal Performed?
A straightforward and efficient method of treating a tongue tie is tongue tie excision, also known as frenotomy. It involves cutting or releasing the tight frenulum that is restricting the movement of the tongue. There are several ways to accomplish this, but the most popular ones are as follows:
- Laser Frenotomy: This technique uses a laser to release the frenulum. It is minimally invasive, requires little to no anesthesia, and generally causes less bleeding and discomfort compared to traditional methods. Laser frenotomy also has a quicker recovery time.
- Scalpel Frenotomy: A scalpel may be used for a more traditional approach. This procedure is generally done under local anesthesia to numb the area, and the frenulum is cut to allow the tongue to move more freely.
- Electrocautery Frenotomy: This method involves using an electric current to cauterize the frenulum and cut through the tissue. It can be effective, though it may cause some discomfort and swelling afterward.
When is Tongue Tie Removal Necessary?
Not every case of tongue tie requires treatment. Many children with mild cases of tongue tie can adapt and learn to use their tongue normally as they grow. However, tongue tie removal may be necessary if the condition leads to significant feeding, speech, or oral health issues. The following are some indications that tongue tie removal could be advantageous:
- Difficulty breastfeeding that persists after a few weeks.
- Problems with speaking or enunciating words clearly.
- A limited range of motion of the tongue, making it difficult to clean the teeth or enjoy certain foods.
- Oral hygiene difficulties leading to an increased risk of cavities or gum disease.
The procedure is typically quick and straightforward, and recovery is usually fast, with most children returning to normal activities within a few days. For infants, breastfeeding can often improve immediately after the procedure, as the baby gains better control of the tongue and latch.
Treating Lip Tie: What to Do?
In some cases, a lip tie may also require treatment, particularly if it is affecting breastfeeding or causing dental issues. This procedure is usually performed in a dentist’s or oral surgeon’s office and can be done with a scalpel or laser.
Final Thoughts: Why Early Intervention Matters
Both tongue tie and lip tie can lead to a range of complications, from breastfeeding difficulties to speech and dental issues. If you or your child are experiencing any symptoms related to these conditions, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can evaluate the situation and recommend appropriate treatment.
For infants, early intervention with tongue tie removal can improve breastfeeding outcomes and prevent long-term feeding issues. In older children and adults, addressing tongue or lip tie may help resolve speech issues, improve oral hygiene, and prevent dental problems.
For more insightful articles related to this topic, feel free to visit- ( Click Here )